
Discord: Search หา message จากข้อมูลหลัก Trillion ยังไง?
ย้อนกลับไปในปี 2017 Discord เริ่มเปิดตัว feature message search เป็นครั้งแรก เป็น feature ที่ user เรียกร้องกันมากในตอนนั้น ทีมของ Discord จึงเริ่มออกแบบระบบที่สามารถรองรับ search บน message ระดับ “trillions message” ได้ในช่วงเริ่มต้น
การเลือกเทคโนโลยี
ทีม Discord เลือกใช้ Elasticsearch เพื่อเป็น backend ของระบบค้นหา ซึ่งเป็น open source ที่ทีมงานมีประสบการณ์ร่วมกันอยู่แล้ว Discordเคยพิจารณาโซลูชันแบบ managed SaaS มาก่อน แต่พบว่ามีค่าใช้จ่ายสูง และทีม Discord กังวลเกี่ยวกับการนำข้อมูล message ของ user ไปเก็บไว้กับ third-party
Elasticsearch เป็นระบบที่แบ่งข้อมูลออกเป็น index โดยในระบบของ Discord จะแยก index ตาม guild หรือ “DM” (direct message) ซึ่งทำให้สามารถค้นหาภายใน resource เดียวได้รวดเร็วโดยไม่ต้องกระจาย search ไปทั่ว cluster
Lazy Indexing เพื่อประหยัด Resources
ทีม Discord เลือกใช้วิธีการ lazy indexing — หมายความว่า Discord จะไม่ index message ทั้งหมดทันที แต่จะทำ historical indexing เมื่อมี search เกิดขึ้นครั้งแรก และหลังจากนั้นจะ index message ใหม่แบบ real-time เฉพาะ guild หรือ DM ที่มี search เท่านั้น
เพื่อรองรับการ index แบบ real-time ทีม Discord ได้สร้าง message queue ที่ให้ worker ดึง message ออกมาเป็น batch แล้วทำการ index แบบ asynchronous ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการใช้งาน Elasticsearch โดยใช้ bulk indexing API
การออกแบบ Index และ Shard
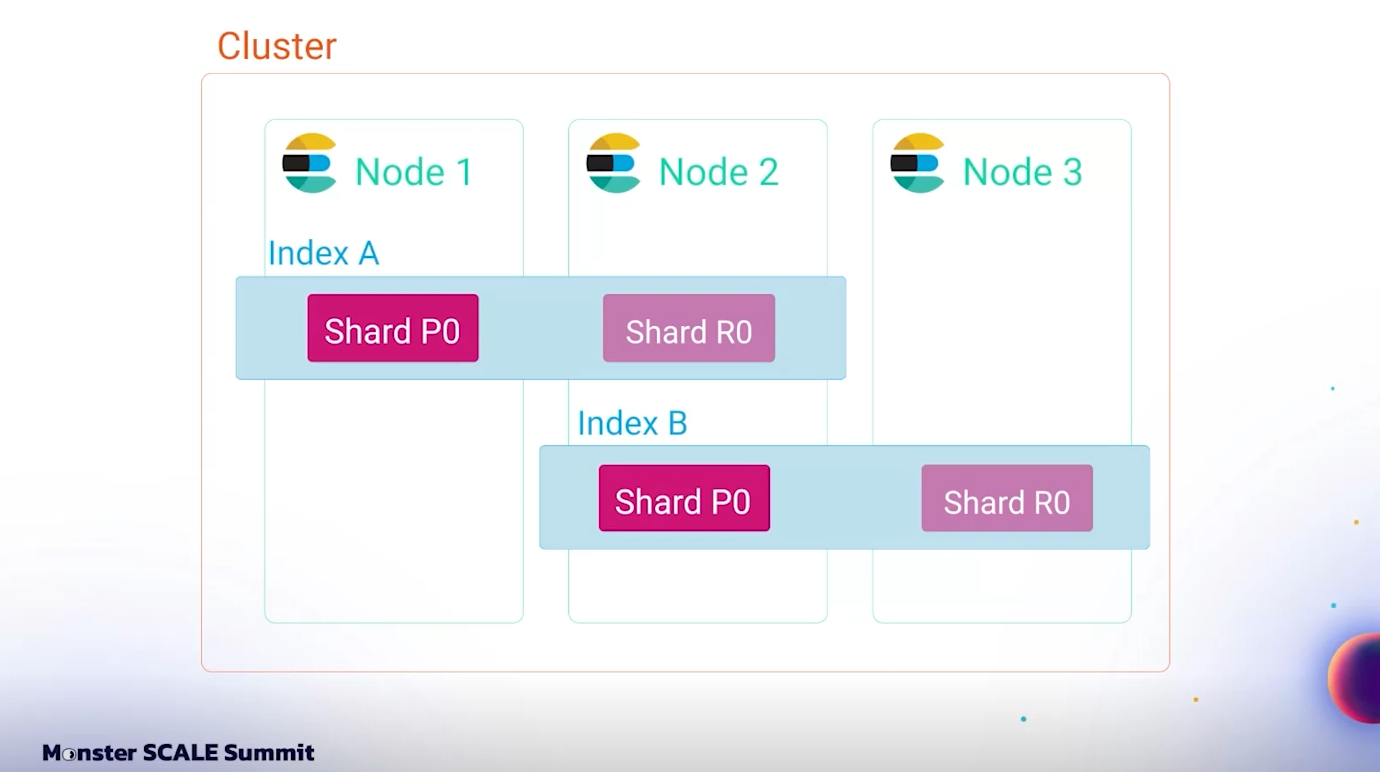
หนึ่งในการตัดสินใจที่สำคัญคือการจัดกลุ่ม message ตาม guild หรือ DM แต่ละอันจะถูกผูกกับ index เพียงหนึ่ง index และภายใน index นั้นจะมีเพียงหนึ่ง primary shard เท่านั้น ซึ่งช่วยให้ทีม Discord สามารถตอบ query ได้โดยไม่ต้อง fan-out ไปหลาย node ใน cluster
โครงสร้างของ Elasticsearch
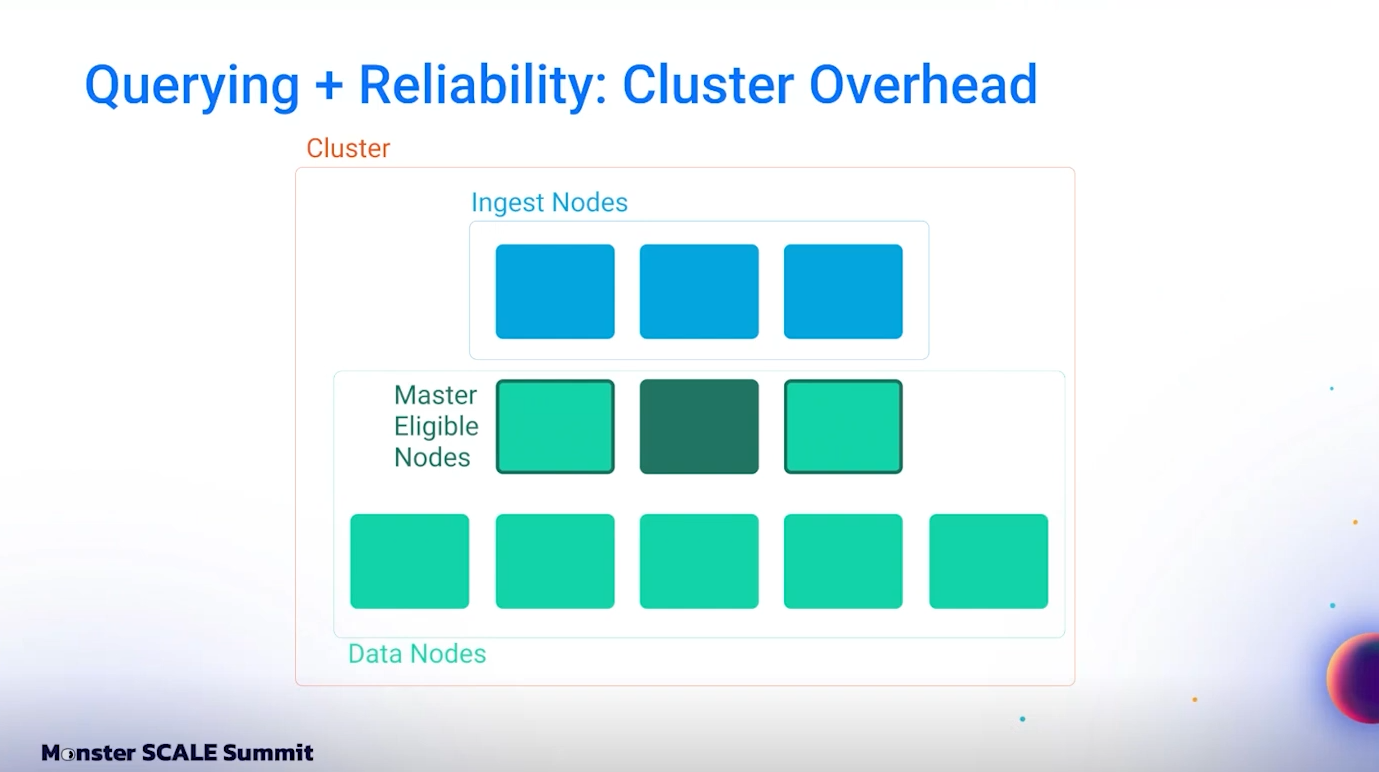
Elasticsearch cluster ประกอบด้วยหลาย node แต่ละ node อาจทำหน้าที่แตกต่างกัน เช่น:
- Master node: ทำหน้าที่ควบคุม coordination ของ cluster
- Ingest node: รับคำขอ query และ index แล้ว route ไปยัง data node
- Data node: เก็บข้อมูลจริงของ shard และตอบสนองต่อ search
แต่ละ index จะมี shard ซึ่งเป็น Lucene inverted index โดย 1 shard จะอยู่บน node เดียวเท่านั้น และสามารถมี replica ได้
ในระบบของ Discord ทางทีมได้ออกแบบให้แต่ละ index มีเพียง 1 primary shard และ 1 replica ช่วยให้การจัดการง่ายขึ้น และทุก message query สามารถเข้าถึง shard ได้โดยตรงใน node เดียว ทำให้ latency ต่ำและ throughput สูง
Search V2: การ Optimization Search System ของ Discord
เปลี่ยนจาก Redis ไปใช้ PubSub เป็น message queue
จุดเริ่มต้นของการแก้ปัญหาคือการย้ายจาก Redis ไปใช้ PubSub ซึ่งมีความสามารถในการ รับประกันการส่ง message (guaranteed message delivery) และสามารถรองรับ backlog จำนวนมากได้โดยไม่ทำให้ message ถูก drop อีกต่อไป ถึงแม้การล่มของ Elasticsearch จะทำให้ indexing ช้าลง แต่จะไม่ทำให้ข้อมูลหายไปเหมือนเดิมอีกแล้ว
ปรับวิธีการทำ bulk indexing ให้ localized มากขึ้น
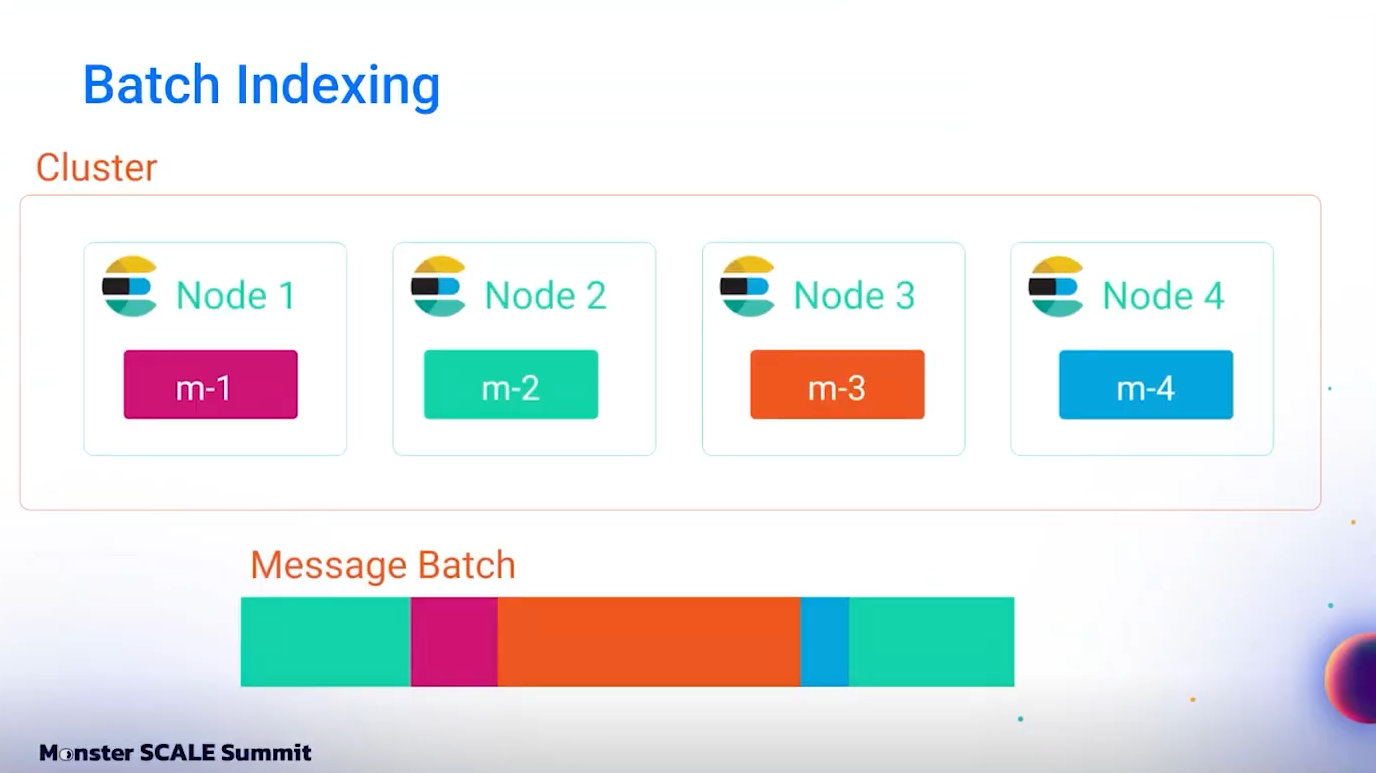
ทีมยังใช้ bulk indexing อยู่ แต่ได้เปลี่ยนกลยุทธ์ใหม่โดยใช้ message router ที่เขียนด้วยภาษา Rust router นี้จะอ่าน message จาก PubSub แล้ว group message ตาม destination ซึ่งในบริบทนี้คือ Elasticsearch cluster และ index ที่ message นั้นจะถูกส่งไป
เมื่อ message router พบ destination ใหม่ มันจะ spawn unbounded channel และสร้าง tokio task หนึ่งตัวเพื่อรอรับ message ทั้งหมดที่มาจาก destination นั้น message ทั้งหมดใน channel เดียวกันนี้จะถูกจัด batch แล้วทำ bulk index ไปยัง node เดียวเท่านั้น ซึ่งหาก node ล้ม ก็จะกระทบแค่ batch เดียวนั้น ทำให้ระบบมีความทนทานต่อ failure มากขึ้นกว่าเดิมหลายเท่า
ในระบบเดิม batch ของ 50 message อาจกระจายไปยัง 50 nodes และล้มทั้ง batch หากมีเพียง 1 node ล้ม แต่ในระบบใหม่ message ถูกจัด batch ตาม destination ทำให้ปัญหานี้หายไปอย่างสิ้นเชิง
/// MessageRouter routes messages to a set of dynamically spawned destinations.
/// This is a simplified representation of the MessageRouter used to index
/// new Discord messages into Elasticsearch.
struct MessageRouter<DestinationKeyT, MessageT> {
destinations: RwLock<HashMap<DestinationKeyT, UnboundedSender<MessageT>>,
}
impl<DestinationKeyT, MessageT> MessageRouter {
/// Attempts to send the message to the given destination, spawning it
/// if the destination does not exist.
fn send_message(
&self,
destination_key: DestinationKeyT,
message: MessageT,
) -> Result<()> {
let mut destinations = self.destinations.write();
match destinations.entry(destination_key) {
Entry::Occupied(mut ent) => {
// Send the message to the given destination
ent.get().send(message).ok();
}
Entry::Vacant(ent) => {
// Spawn a new destination and receiver
let (destination_sender, destination_receiver) = unbounded_channel();
let task = tokio::task::spawn(async move {
// Destination task receives messages with same destination
// key on destination_receiver.
// For our case, the destination task groups messages into
// chunks and bulk indexes into Elasticsearch.
});
ent.insert(destination_sender).send(message).ok();
}
}
Ok(())
}
}ย้ายระบบขึ้น Kubernetes พร้อม Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK)

อีกหนึ่งการตัดสินใจเชิง Architecture ที่พลิกเกม คือการย้ายระบบ search ทั้งหมดขึ้นไปอยู่บน Kubernetes โดยใช้ Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) ซึ่งเป็น operator สำหรับ orchestrating Elasticsearch บน Kubernetes
ECK ช่วยให้ Discord กำหนด topology ของ cluster ได้ชัดเจน เช่น จำนวน master nodes, ingest nodes, และ data nodes แต่ละประเภทสามารถกำหนด resource ตาม workload ได้ และยังทำ rolling upgrade ได้อย่างปลอดภัยแบบไม่มี downtime ซึ่งเป็นสิ่งที่ระบบเดิมไม่สามารถทำได้เลย
OS upgrades สามารถทำผ่าน rolling restart ของ node pool โดยไม่ต้อง stop ทั้ง system
Multi-cluster Cell Architecture: แนวคิดใหม่เพื่อ scale และ isolate
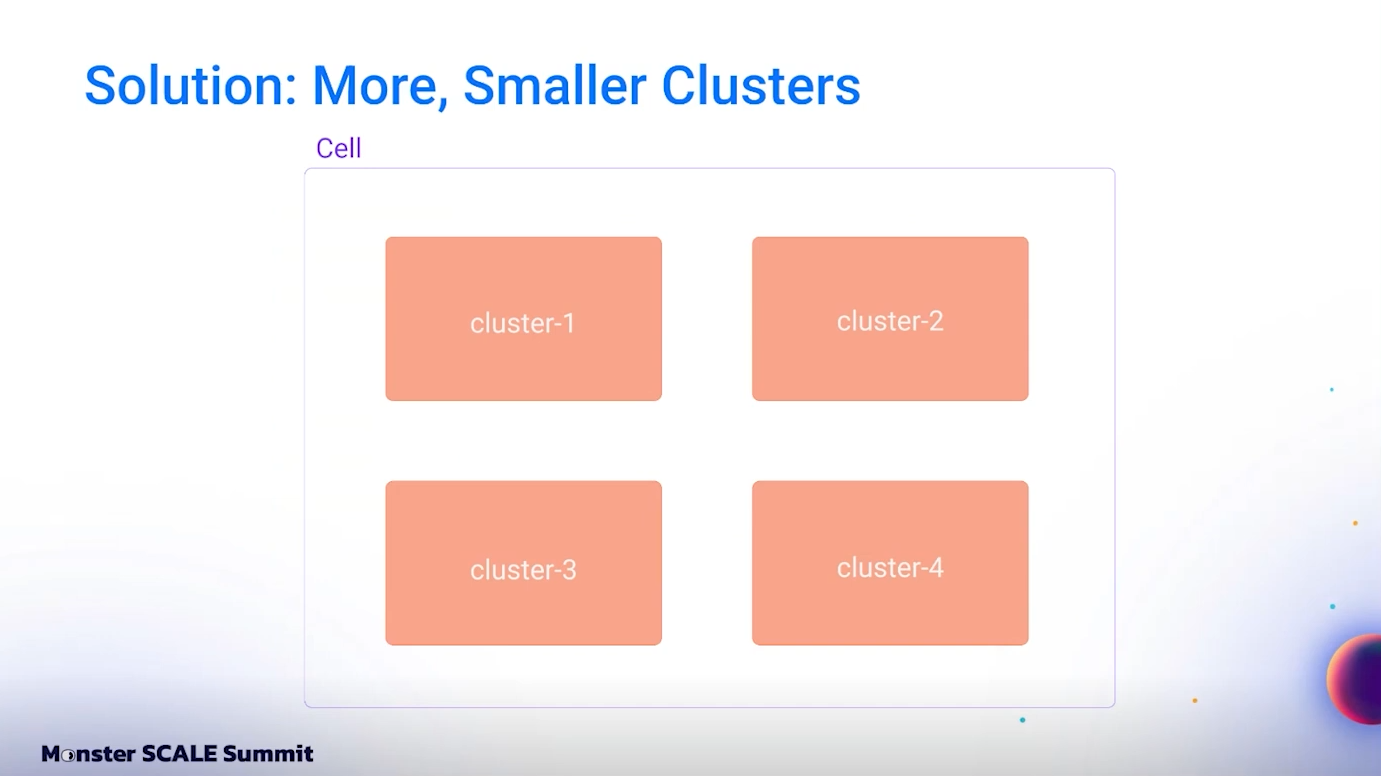
เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาที่เคยเกิดกับ cluster ใหญ่ที่รวมทุกอย่างไว้ที่เดียว ทีม Discord จึงแยกออกเป็น cell architecture ซึ่งในที่นี้ cell คือกลุ่มของ Elasticsearch clusters หลายชุด โดยแต่ละชุดมีหน้าที่จัดการกับข้อมูลเฉพาะด้าน เช่น:
- cell หนึ่งสำหรับจัดการ message จาก guild
- cell หนึ่งสำหรับ DM messages ซึ่ง shard ตาม user แทน channel
แนวคิดนี้ทำให้ทีมสามารถ index และ search message ในมิติใหม่ เช่น cross-DM search หรือ search ข้าม direct message ทั้งหมดที่ user เคยมี ซึ่งไม่สามารถทำได้ในระบบเดิมที่ shard ตาม channel
cell แต่ละชุดประกอบด้วย ingest nodes, master-eligible nodes และ data nodes ซึ่งแยกกันอย่างชัดเจนเพื่อป้องกันการเกิด bottleneck และลด coordination overhead โดยสามารถเลือกขนาดของ cluster แต่ละชุดให้เหมาะกับ workload ของตนได้
ตัวอย่างเช่น guild ปกติอาจใช้ cluster เล็กๆ ที่มี 1 primary shard ต่อ index แต่สำหรับ Big Freaking Guilds (BFGs) ที่มี message หลาย trillions message จะใช้ index ที่มี multiple primary shards เพื่อรองรับการ fan-out query แบบขนานได้
การจัดการ Big Freaking Guilds (BFGs)
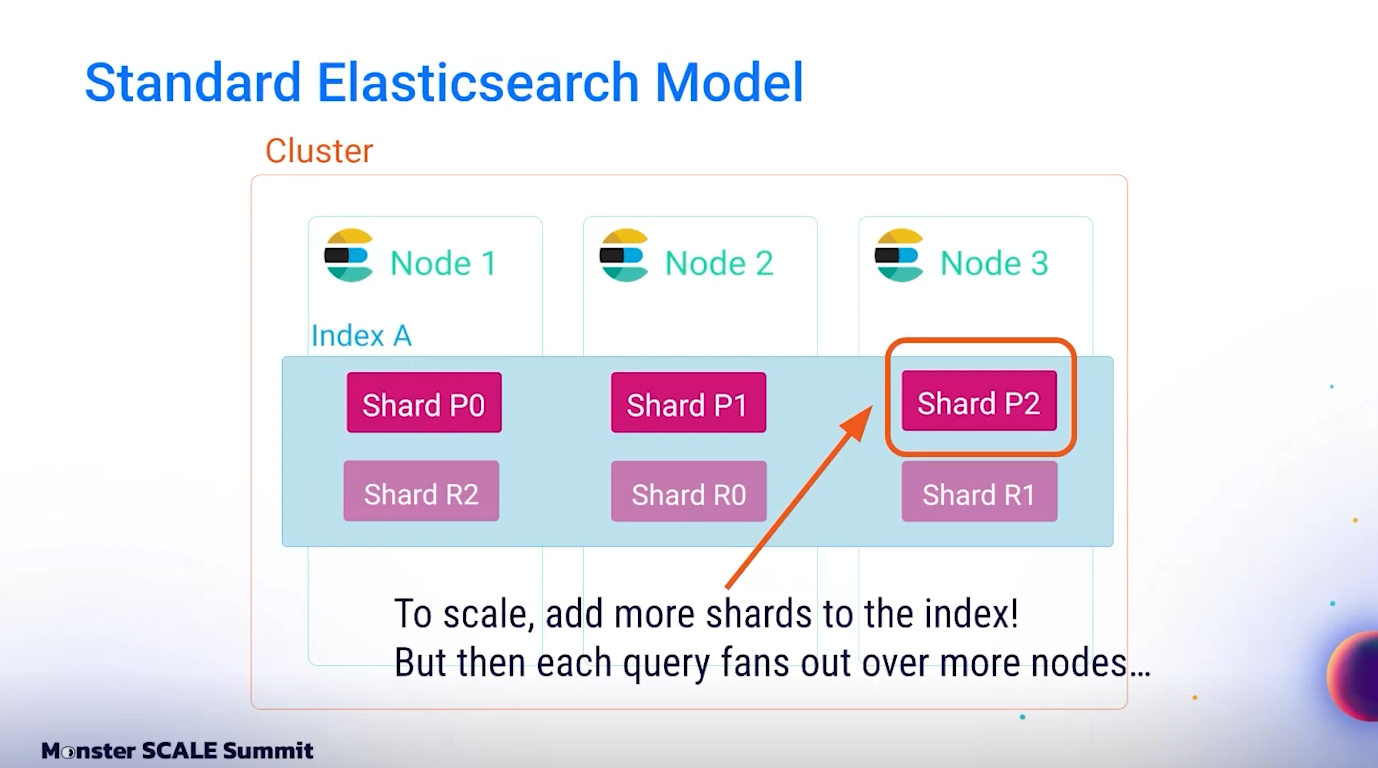
ในระบบ Search V1 ทีม Discord ออกแบบให้ guild หนึ่งถูกผูกกับ index เดียว ซึ่งภายใน index นั้นจะมี 1 primary shard และ 1 replica แนวทางนี้มีข้อดีคือ query ใด ๆ ภายใน guild นั้นสามารถเข้าถึงได้ใน node เดียว โดยไม่ต้อง fan-out หรือประสานข้อมูลข้าม shard ซึ่งช่วยให้ latency ต่ำมาก
แต่สำหรับ guild ที่มี message เกิน 2 trillions Lucene จะไม่สามารถ index เพิ่มเติมได้อีกเลย การแก้ปัญหาชั่วคราวใน Search V1 คือให้ทีม Safety ตรวจสอบและลบ guild ที่เป็น spam เพื่อให้ space ที่ว่างกลับมา แต่แน่นอนว่าทีม Discord ไม่สามารถใช้วิธีนี้ในระยะยาวกับชุมชน user งานจริงที่มี message ปริมาณมหาศาลได้
ใน Search V2 ทีมได้สร้างกลไกการ reindex สำหรับ BFGs ที่สามารถ ย้ายข้อมูลจาก index เก่าไปยัง index ใหม่ที่มีหลาย primary shards ได้โดยไม่ต้อง stop service หรือ stop indexing message ใหม่
ขั้นตอนการ reindex มีดังนี้:
- ตรวจจับว่า guild ใดใกล้จะชน
MAX_DOClimit ซึ่งปกติถูกเก็บอยู่ในindex-a - สร้าง
new-bfg-indexที่มีจำนวน primary shard มากกว่าเดิม 2 เท่า - เริ่มทำ dual-indexing โดย message ใหม่จะถูก index ทั้งใน
index-aและnew-bfg-index - เริ่ม job สำหรับ historical reindex โดยค่อย ๆ นำ message เก่าจาก guild นี้ไปใส่ใน
new-bfg-index - ขณะ historical index ดำเนินอยู่ ระบบยังคงตอบ query จาก
index-aตามปกติ - เมื่อ historical index เสร็จสมบูรณ์ และมั่นใจว่า
new-bfg-indexทำงานได้ดี จะสามารถเปลี่ยน traffic query ไปยัง index ใหม่ - จากนั้นจะหยุด dual-indexing แล้วลบ message ทั้งหมดออกจาก
index-a
ด้วยวิธีนี้ BFGs จะสามารถใช้ index ใหม่ที่มีหลาย shards ซึ่งช่วยให้ search query สามารถ parallelize ได้ และเพิ่ม throughput ได้มากกว่าระบบเดิมที่ใช้ shard เดียว
ผลลัพธ์ของ Search V2: เปลี่ยนเกมอย่างแท้จริง
หลังจากเปิดใช้งานระบบ Search V2 เต็มรูปแบบ Discord สามารถ index message ระดับ trillions message ได้จริง และที่สำคัญคือ throughput เพิ่มขึ้น มากกว่าสองเท่า จากระบบเดิม
latency โดยรวมดีขึ้นชัดเจน: จาก median latency 500ms ใน Search V1 เหลือเพียง น้อยกว่า 100ms ใน Search V2 ส่วน P95 และ P99 ลดลงจากประมาณ 1 วินาที เหลือเพียง ไม่ถึง 500ms
Discord สามารถทำ rolling upgrade ได้แบบไม่มี downtime ทำให้ระบบสามารถรับ patch ใหม่ ๆ ได้ทันเวลา เช่นกรณี log4shell ที่เคยทำให้ Search V1 ต้องหยุดระบบทั้งระบบเพื่อ patch log4j แต่ใน Search V2 ทำได้ทันทีโดยไม่กระทบ user เลยแม้แต่น้อย
ทุกวันนี้ Discord ใช้ Elasticsearch clusters กว่า 40 clusters กระจายออกเป็น cells หลายชุด และภายในมี indices นับพัน เพื่อรองรับ message ทั้งจาก guild, DM, BFG และ use case ใหม่ ๆ อย่าง cross-DM search
จาก search system ที่เคยเปราะบางและยากต่อการ scale, Discord ได้สร้าง Search V2 ที่สามารถ scale ได้ในระดับ global พร้อมความเร็ว ความทนทาน และความสามารถในการดูแลรักษาได้อย่างมืออาชีพ
หากคุณเป็น engineer ที่กำลังออกแบบระบบค้นหาของตัวเอง หวังว่าบทเรียนจาก Discord เรื่องนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจว่าการออกแบบ search infrastructure ที่ดีนั้นไม่ได้ขึ้นอยู่กับการเลือกเทคโนโลยีเพียงอย่างเดียว แต่อยู่ที่การเข้าใจ workload, การ shard ข้อมูลอย่างถูกต้อง, และการรองรับ failure อย่างเป็นระบบ